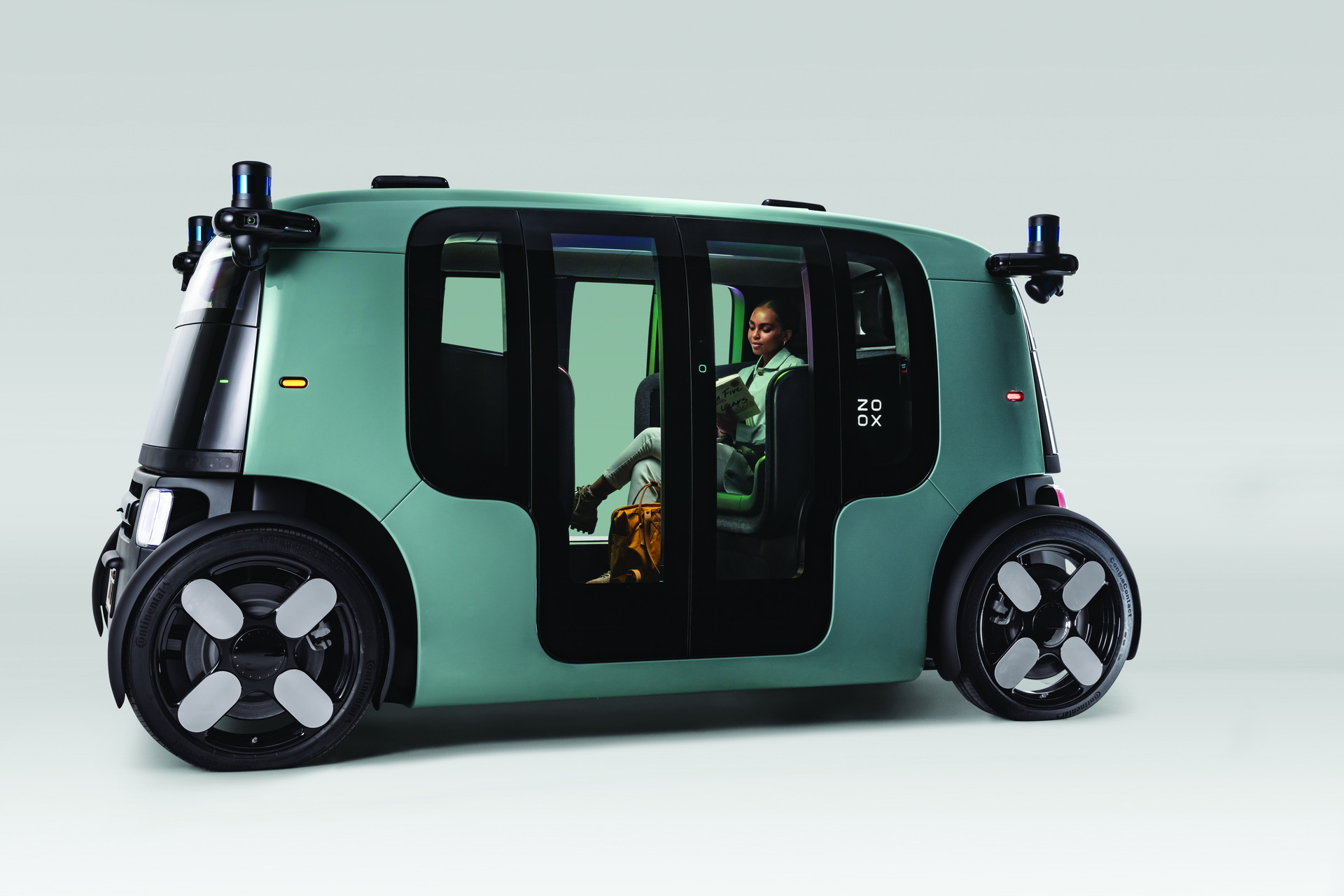
As the world moves towards autonomous vehicles, researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have found that the computing power required to run these vehicles could make them quite carbon-intensive. In fact, if the mass adoption of autonomous vehicles occurs, it could generate as many greenhouse gas emissions as all the world’s data centers combined produce, the study found.
The study’s authors found that these vehicles could use a considerable amount of computer power, with a 360-degree view of the world and 20 cameras trying to understand all the things happening at the same time. To understand the impact of autonomous vehicles on carbon emissions, the researchers looked at an autonomous vehicle with ten cameras, whose data is being processed by ten deep neural networks. After one hour of driving, the vehicle would make 21.6 million inferences.
See also: ServCity Project Successfully Completes 1,600 Autonomous Miles in London with Nissan Leaf
“These vehicles could actually be using a ton of computer power,” Sertac Karaman, one of the study’s coauthors, told DeZeen. “They have a 360-degree view of the world, so while we have two eyes, they may have 20 eyes, looking all over the place and trying to understand all the things that are happening at the same time.”
If a billion autonomous vehicles were on the world’s roads, the global fleet would make 21,600 trillion inferences per hour. In a scenario where there are a billion autonomous vehicles on the roads, driving for an hour a day, the power required to process all of that data would emit the equivalent of approximately 0.14 gigatons per year or 0.3% of all global emissions.
However, the study’s authors believe that finding efficiencies in algorithmic development and more specialized hardware could help reduce the carbon footprint of autonomous vehicles. They suggest designing more efficient autonomous vehicles that have a smaller carbon footprint from the start.
See also: Haomo.AI Technology Unveils DriveGPT, a New AI Foundation Model for Self-Driving Cognition
While this study may seem concerning, it is worth noting that the emissions from autonomous vehicles would still be significantly less than what internal combustion vehicles currently produce. Nonetheless, the authors urge us to consider the environmental impact of autonomous vehicles and ensure that the technology is developed in a sustainable way.