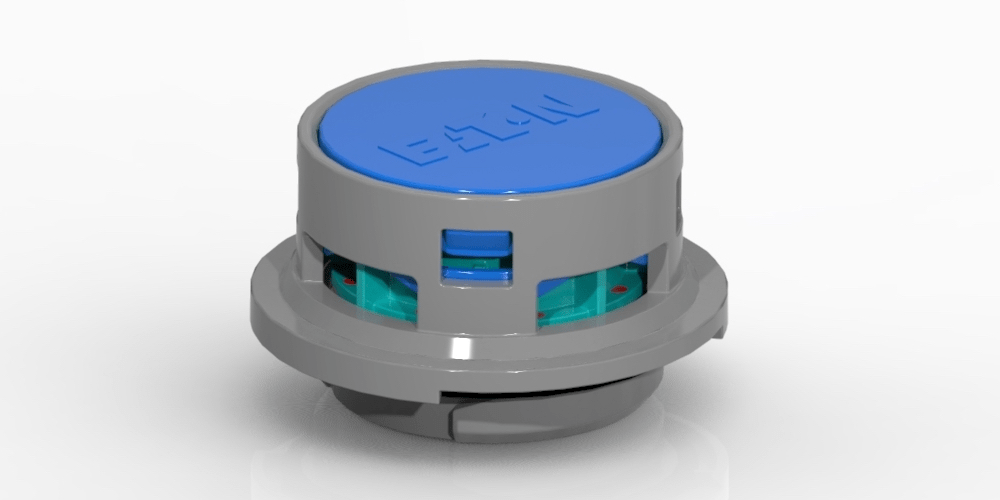
Eaton has announced the launch of its latest product for the electric vehicle (EV) market – a 3-in-1 vent valve designed to simplify the assembly process of EV batteries. This new technology combines three functions – a mechanism to check the tightness of the battery housing, passive and active venting to relieve excess pressure, and a leak-check feature.
What’s more, the valve has been designed to be flexibly installed using a spring-based actuation technology, which allows Eaton to accommodate different opening pressure requirements with the same valve design.
See also: Ford will introduce seven new electric vehicles in Europe by 2024
The venting function is particularly noteworthy, as it eliminates the need to install a vent valve as the final step of the battery assembly process, which is currently standard in today’s EV architectures. Eaton’s new technology offers a more thorough leak-testing solution, which includes testing the sealing surface of the vent itself when the battery vent valve is already assembled, a feature that Eaton claims is missing from traditional methods.
Eaton’s new vent valve technology can be assembled either through a quick-connect feature or by a screwed metal-to-metal connection, providing customers with the freedom to choose their preferred assembly method while ensuring a sturdy connection that stays in place.
The company’s Vehicle Group manager, Jens Buhlinger, expressed his excitement about the product’s launch, stating that “We’re excited to offer a 3-in-1 technology that helps ensure the system integrity of increasingly powerful EVs.”
See also: Kia Corp to build electric vehicles in the US from 2024 to get EV tax credit
This new product development follows Eaton’s recent $4.9 million grant from the US Department of Energy to reduce the cost and complexity of DC charging infrastructure. The company is leveraging its long-standing expertise, research, and partnerships to fast-track the electrification of transport by reducing the steps required to connect charging systems directly to the utility distribution system.