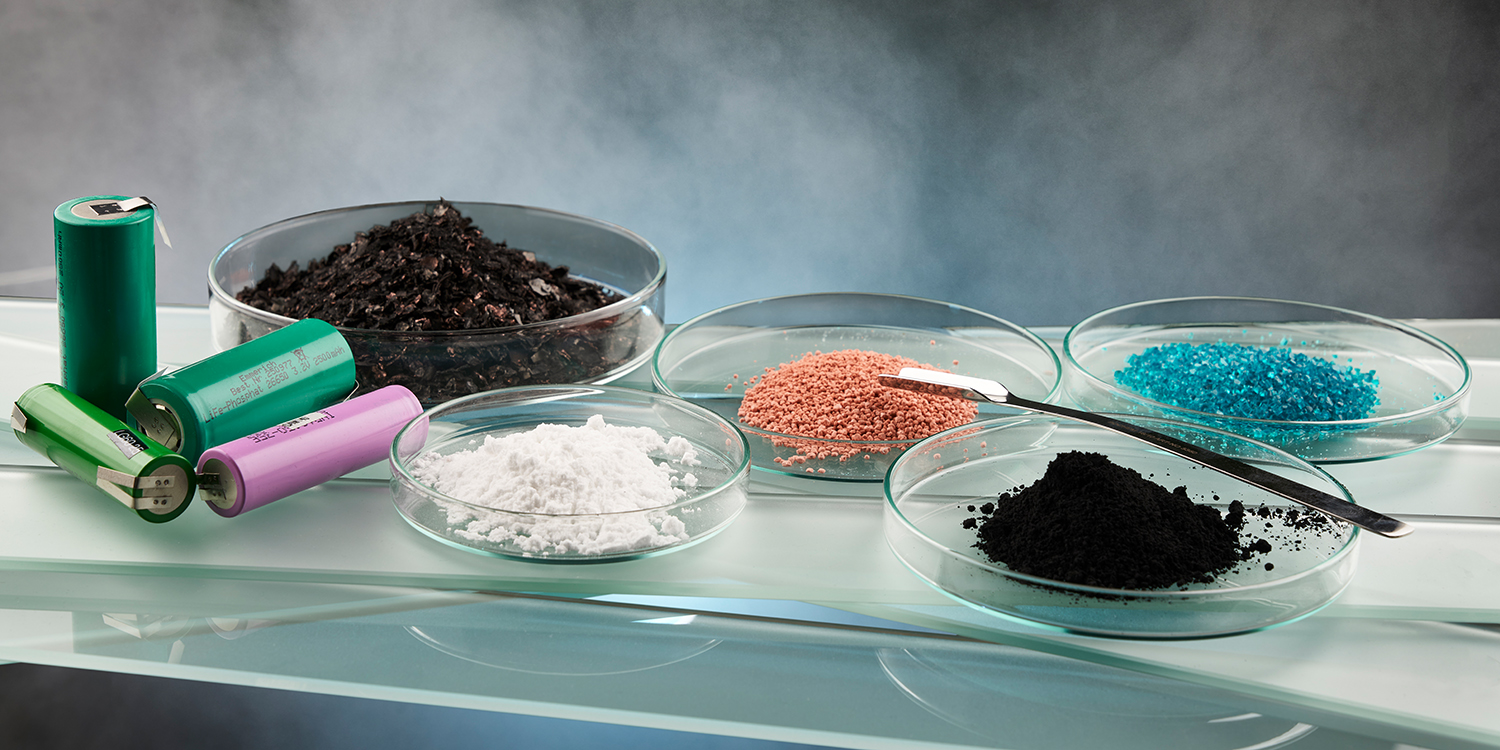
In a significant step towards sustainable battery recycling, researchers at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) have developed a process that recovers up to 70% of lithium from used batteries without the use of corrosive chemicals or high temperatures. The groundbreaking process involves a mechanochemical reaction that takes place at room temperature using aluminium as a reducing agent. This eliminates the need for prior sorting of materials and allows for the cost-effective and environmentally friendly recycling of different commercially available lithium-ion batteries.
Lead author of the publication, Oleksandr Dolotko, explains that the method is suitable for recovering lithium from cathode materials of different chemical compositions, making it applicable to many different lithium-ion batteries. “It allows for cost-effective, energy-efficient and environmentally friendly recycling,” he adds. The process involves grinding up battery waste to form metallic composites with water-soluble lithium compounds, which are then dissolved in water and heated to remove the water by evaporation.
One of the key advantages of the KIT process is that it takes place at normal air pressure, making it energy-efficient and simple enough for use on an industrial scale. According to the researchers, the process is not only environmentally friendly but also cost-effective, providing a viable solution for the sustainable recycling of lithium-ion batteries.
The KIT researchers worked alongside scientists from the Institute for Applied Materials – Energy Storage Systems (IAM-ESS) and the Helmholtz Institute Ulm for Electrochemical Energy Storage (HIU) as well as energy company EnBW to develop the innovative process.
Speaking about the breakthrough, Dr. Stefano Passerini, Director of the IAM-ESS, said, “This is a significant step towards a sustainable future for lithium-ion batteries. The process is cost-effective, energy-efficient, and environmentally friendly, making it a viable solution for the recycling of used batteries on an industrial scale.”
See also: Horizon Robotics and GAC AION Sign Strategic Partnership to Develop Driving Assistance Products
With the increasing demand for lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles and renewable energy systems, the need for sustainable battery recycling has never been more pressing. The KIT process represents a significant breakthrough in this field, offering a practical and cost-effective solution for the recovery of valuable materials from used batteries.