In the realm of electric vehicles (EVs), concerns about the long-term effects of DC fast charging on high-voltage batteries have lingered among owners. A pertinent question arises: how does frequent use of fast charging impact battery degradation over time? Recent research sheds light on this pressing matter, uncovering crucial insights for EV enthusiasts.
A comprehensive study conducted by Recurring Auto, a leading provider of vehicle and battery analysis reports for EVs, has delved into the impact of charging methods on battery health. Analyzing charging data from a substantial pool of over 12,500 Tesla vehicles in the United States, the study aimed to discern the potential disparity in battery degradation rates between Direct Current (DC) fast charging and Alternating Current (AC) charging, commonly referred to as ‘Level 1’ or ‘Level 2’ charging.
By segregating vehicles based on their charging behavior – classifying those frequently employing fast charging (at least 90 percent of the time) and those using it sparingly (less than 10 percent) – Recurring Auto endeavored to unravel any discernible variance in the degradation patterns between the two methods.
The findings of the study unveiled a noteworthy revelation: the rate of range degradation exhibited statistically similar trends between the two charging approaches. Among the models investigated, including the Tesla Model 3 and Tesla Model Y, no significant discrepancy emerged in terms of battery health between EVs predominantly subjected to DC fast charging and those predominantly relying on AC charging.
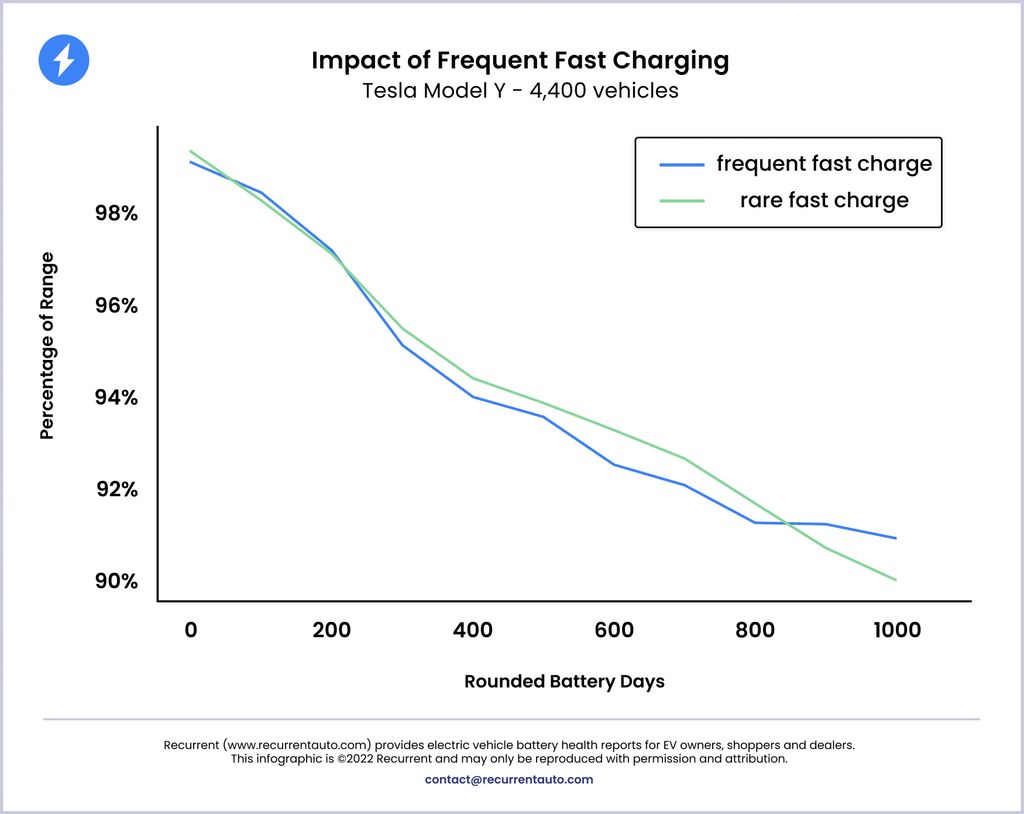
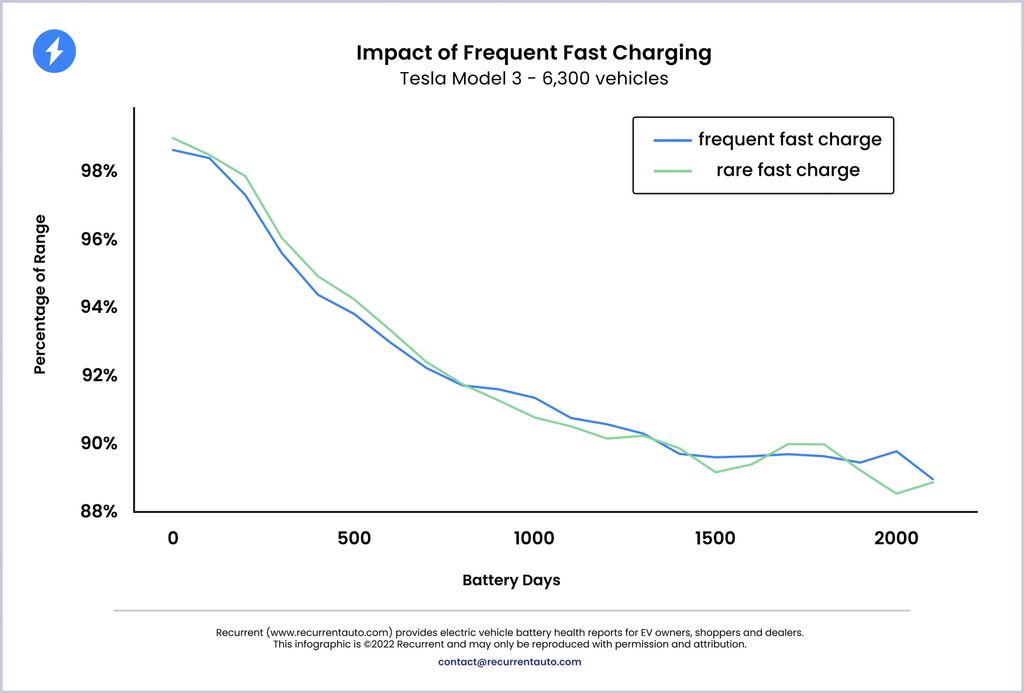
Graphical representations showcased the percentage of the original range displayed on the vehicles’ dashboards, juxtaposed against the passage of time in days. These visual depictions further accentuated the consistent degradation trends observed across the charging methodologies, reaffirming the study’s central conclusion.
Beyond the choice between DC and AC charging, the research emphasized the multifaceted nature of battery health preservation. Extremes of temperature, as well as operating at very low or high states of charge, emerged as crucial variables impacting battery longevity.
Nevertheless, the study underscored the safeguarding measures integrated into EVs by manufacturers. These encompass robust thermal management systems, sophisticated voltage control, and adept battery management systems. These features collectively mitigate the risks associated with routine fast charger utilization, ensuring sustained battery health over time.
For EV owners keen on extending the lifespan of their batteries, leveraging the preconditioning feature emerged as a pivotal practice. This feature, applicable in both extreme heat and cold conditions, optimizes battery temperature before initiating the charging process. Additionally, experts advised against engaging in fast charging at battery states with very low or high charge levels, as heightened battery resistance under these circumstances can exert undue strain on the battery.
Highlighting a previous study from 2020, the research landscape surrounding battery degradation in EVs and Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) becomes more comprehensive. In this earlier investigation, battery-powered vehicles demonstrated degradation ranging from zero percent to 4.1 percent within the initial year of usage. Notably, the 2019 Chevrolet Bolt EV emerged as the best-performing model, while the 2019 Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV faced greater battery degradation challenges.
As the electric mobility landscape continues to evolve, studies of this nature furnish EV enthusiasts with crucial insights to make informed decisions regarding charging practices and overall battery care. Amid these findings, EV owners can rest assured that advancements in battery management systems and prudent charging practices combine to sustain the health and longevity of their prized electric vehicles.

