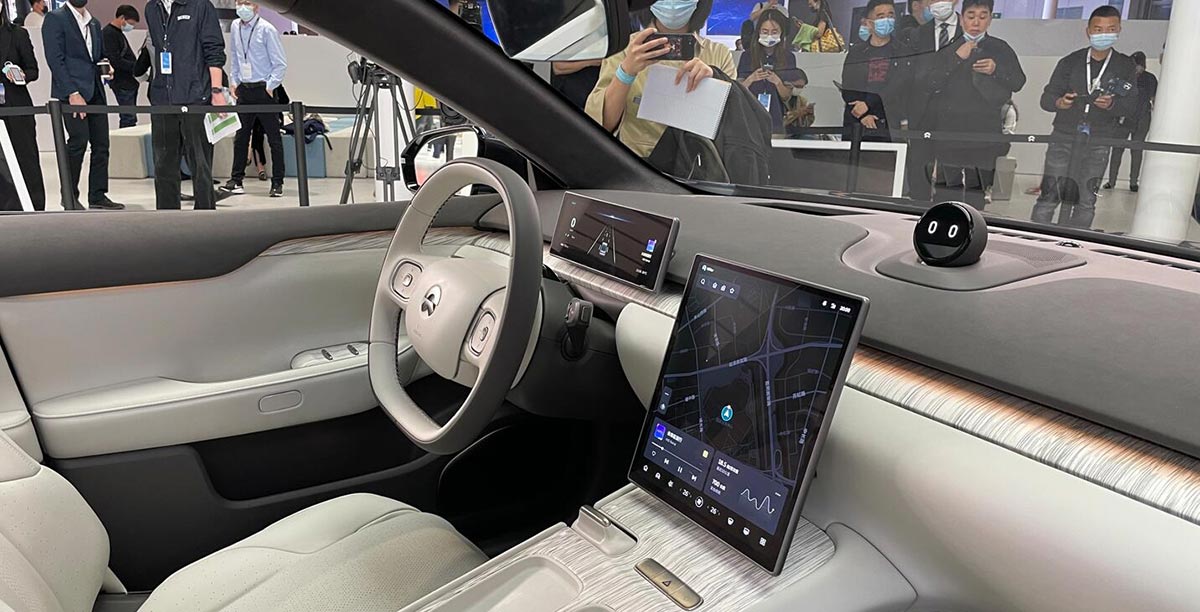
NIO is reportedly entering into a joint venture with battery specialist SVOLT, aiming to embark on the development of large cylindrical battery cells. This development, revealed by Chinese media outlet 36kr and based on insights from informed industry insiders, includes plans for establishing a pilot production line in Maanshan, within the Anhui province of China, as well as the formation of a collaborative research and development team.
NIO’s initial intention was to construct a battery factory with a substantial annual capacity of 40 gigawatt-hours (GWh) for the production of large cylindrical cells, situated alongside its primary production center in Hefei, Anhui. However, in July, NIO disclosed the postponement of its self-developed electric car battery production schedule.
According to reports from 36kr, the joint venture with SVOLT has been instigated due to setbacks in NIO’s internal battery development endeavors. Some sources even suggest that NIO has encountered significant challenges in its battery project. SVOLT, a battery manufacturer previously spun off from Great Wall Motor, is known to have global ambitions in the battery sector. The initial plan between NIO and SVOLT encompasses investments in a pilot production line in Maanshan and the consolidation of a portion of their research and development resources. Notably, both parties intend to maintain their independence concerning manufacturing and procurement processes.
The collaborative project is envisioned as a trial of a new partnership model, primarily focusing on preliminary testing and development, as stated in the report. For NIO, this venture represents a final attempt at forward integration into battery cell production.
In July, the same Chinese portal reported NIO’s cautious approach to new investments, attributed to relatively modest sales figures for its electric vehicles, a sharp decline in lithium prices, and a less pressing need for battery procurement, as insiders revealed.
NIO had previously announced its intention to commence in-house battery pack manufacturing by 2024, with long-term plans to produce some of its battery cells. Reports indicated NIO’s work on 4680-format battery cells and lower-cost lithium manganese iron phosphate (LMFP) cells, intended for mass production for NIO-branded electric vehicles and its new ALPS brand.
In February 2023, Reuters disclosed NIO’s plans to establish its inaugural battery factory, aiming to produce large cylindrical cells with an annual capacity of 40 GWh adjacent to its primary production center in Hefei, Anhui. This strategic move was aimed at mitigating dependence on its principal cell supplier, CATL, following significant price negotiations in April 2022. Earlier this year, reports emerged of CATL offering lower prices to several manufacturers, including NIO, in exchange for commitments to procure at least 80 percent of their batteries from CATL.
It’s worth noting that NIO’s 75 and 100 kWh battery packs currently utilize CATL cells, with the 100 kWh packs incorporating cells featuring NCM chemistry. The 75 kWh packs are a combination of LFP and NCM cells, strategically placed to enhance battery performance. Additionally, the semi-solid-state cells for NIO’s latest 150 kWh pack are sourced from WeLion.