Tesla has recently released its latest public safety data, including statistics on owners who have activated Autopilot, drawing attention to discussions about the electric vehicle manufacturer’s safety record. The data, which covers the first quarter of 2024, appears to show positive trends for the automaker, although a deeper analysis reveals more nuanced insights.
Autopilot, which encompasses cruise control and lane-keeping assistance features, is a key focus of Tesla’s safety data. It’s important to note that the data does not appear to include users of Full Self-Driving (FSD), a more advanced version of Autopilot labeled as “beta.”
According to Tesla’s internal documentation, the data suggests that drivers and occupants are safer in Tesla vehicles compared to the average vehicle. This conclusion is based on the number of miles driven per accident. In the first quarter of 2024, Tesla recorded one crash for every 7.63 million miles driven with Autopilot engaged, compared to one crash for every 955,000 miles driven without Autopilot.
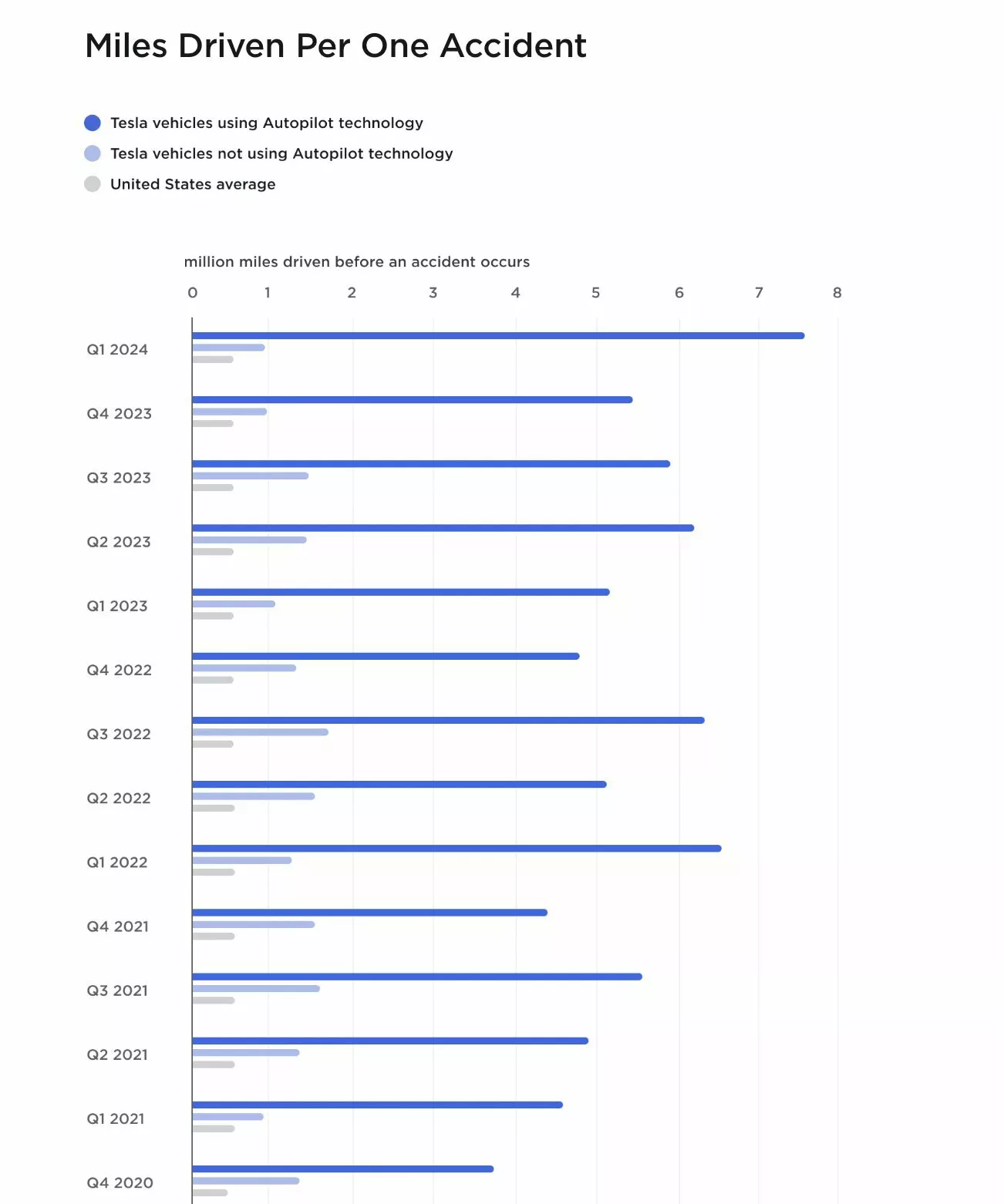
Throughout 2023, Tesla’s data shows that the lowest number of miles driven between accidents with Autopilot engaged was 5.18 million miles, while the lowest figure for Tesla drivers not using Autopilot was 1 million miles. These figures indicate a significant safety improvement when comparing drivers using Autopilot to those not using it.
Tesla’s approach to counting Autopilot accidents includes incidents where the system is deactivated within five seconds of a crash, regardless of fault. Over 35% of the recorded crashes were incidents where a Tesla driver was rear-ended.
However, miles driven between accidents is not a perfect safety metric on its own. Tesla drivers typically engage Autopilot on highways, where road and traffic conditions are more predictable, potentially skewing the comparison with the national average, which includes miles driven on all types of roads.
While these figures suggest a material safety benefit to Tesla owners and occupants, more data, especially from independent third-party sources, is needed to fully understand vehicle safety across different brands.
