The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 (IRA) brought about a significant transformation in the federal tax credit system in the United States, specifically targeting plug-in electric cars. Today, we delve into this pivotal incentive and examine the qualifying criteria for eligible models.
The federal tax credit serves as a substantial incentive, offering up to $7,500 for new plug-in electric vehicles that meet the specified requirements.
Initially introduced in mid-2022, the primary prerequisite was that an electric vehicle must be manufactured in the United States, Canada, or Mexico.
However, as of April 18, 2023, the requirements were expanded and significantly strengthened, with future years expected to impose even more stringent criteria.
As of June 2023, the qualifying criteria include:
- Final assembly in North America: United States, Canada, or Mexico.
- MSRP (Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price) limits:
- SUVs, vans, pick-up trucks: $80,000
- Other vehicles (cars): $55,000
- Income limits for different tax statuses:
- Single: $150,000
- Head of Household: $225,000
- Filing jointly: $300,000
- Battery requirements:
- Critical minerals ($3,750): At least 40% of the critical minerals’ value must be mined, processed, or recycled in the United States (or Free Trade Agreement countries), with relaxed conditions now including Japan.
- Battery components ($3,750): At least 50% of the battery components’ value must be manufactured or assembled in North America.
- Battery capacity: A minimum of 7-kilowatt-hour (kWh) battery.
- Gross vehicle weight rating: Less than 14,000 pounds (6,350 kilograms).
One of the most comprehensive breakdowns of these requirements is presented in the Fact Sheet IRA EV Tax Credits, jointly released by the Electrification Coalition and SAFE.
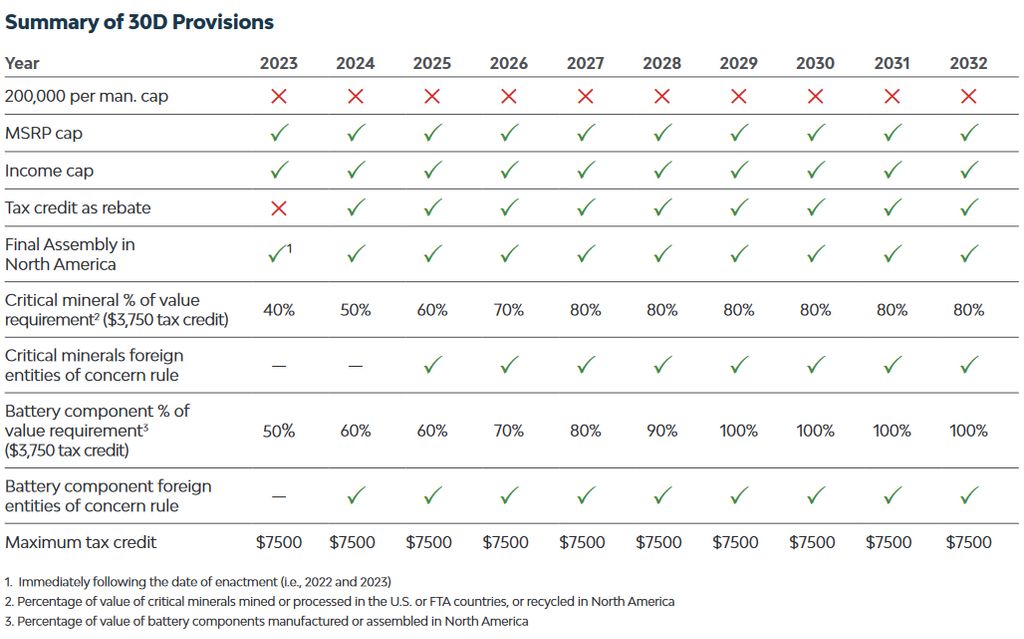
Models that fully comply with the outlined requirements are eligible for the maximum tax credit of $7,500. However, meeting only one of the battery-related criteria (critical minerals or components) reduces the incentive to $3,750.
The maximum tax credit available, depending on meeting the critical mineral and battery component requirements, is as follows:
- EVs meeting both requirements: $7,500
- EVs meeting only one requirement: $3,750
- EVs not meeting the requirements: $0
Starting from 2024, the federal tax credit system will undergo significant improvement, transitioning into a rebate offered at the point of purchase.
Currently, only five manufacturers have been confirmed to qualify for the tax credit incentive: General Motors (Chevrolet and Cadillac), Ford, Rivian, Tesla, and Volkswagen.
The list of eligible models, eligible for either $3,750 or $7,500, is subject to change and as of June 3, 2023, includes:
General Motors (confirmed in April):
- Cadillac Lyriq – up to $7,500
- Chevrolet Blazer EV – up to $7,500
- Chevrolet Bolt EV – up to $7,500
- Chevrolet Bolt EUV – up to $7,500
- Chevrolet Equinox EV – up to $7,500
- Chevrolet Silverado EV – up to $7,500
Ford (confirmed in April):
- Ford E-Transit – up to $3,750
- Ford F-150 Lightning – up to $7,500
- Ford Mustang Mach-E – up to $3,750
Rivian:
- Rivian R1S – up to $3,750
- Rivian R1T – up to $3,750 (*Note: Only a few entry-level versions of the R1S and R1T qualify due to the price cap.)
Tesla (confirmed in April, updated on June 2, 2023):
- Tesla Model 3 – up to $7,500 (all versions, as per the manufacturer as of June 2, 2023)
- Tesla Model Y – up to $7,500
Volkswagen (confirmed in April):
- Volkswagen ID.4 – up to $7,500
Interestingly, some locally produced all-electric cars no longer qualify for the federal tax credit incentive. The Nissan Leaf, for example, lost its eligibility on April 18, 2023, despite being equipped with locally produced lithium-ion battery cells. It seems that the Leaf did not meet the necessary battery-related requirements.
Another instance is the Genesis Electrified GV70, which commenced production in Montgomery, Alabama, in February. As it stands, its battery components are currently sourced from South Korea, rendering it ineligible for the incentive after April 18, 2023. Otherwise, it would have posed strong competition for the imported Genesis GV60 model.
The list of eligible plug-in hybrid car models is even shorter, with only three manufacturers qualifying: BMW, Stellantis (Chrysler/Jeep brands), and Ford (Ford/Lincoln brands).
One particularly important and surprising aspect is that in the case of leasing, customers can still benefit from the full $7,500 federal tax credit, even if a particular model does not meet the aforementioned requirements or if the customer is ineligible.
Numerous reports indicate that lease rates may be reduced by factoring in the incentive at the manufacturer/dealer level and passing the savings to the lessees. Customers can also choose to buy out the car early to lower monthly interest and taxes.
This unique scenario arises due to two distinct sections of the law: the 30D section for individual purchases (including all requirements) and the 45W section for commercial credits (excluding the aforementioned requirements). As per the IRS’ December interpretation, businesses leasing vehicles are permitted to claim the commercial EV tax credit for each leased vehicle, offering a way to pass the full $7,500 federal tax credit to customers.
Examples of this EV tax credit loophole were observed in April for Hyundai and in May for Tesla. Attractive lease deals have also been reported for various models, including the Kia EV6, Hyundai Ioniq 5/Ioniq 6, and Tesla Model 3. It is likely that many brands have already begun offering enticing deals to capitalize on this solution.