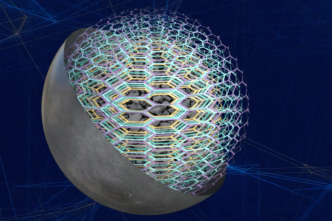
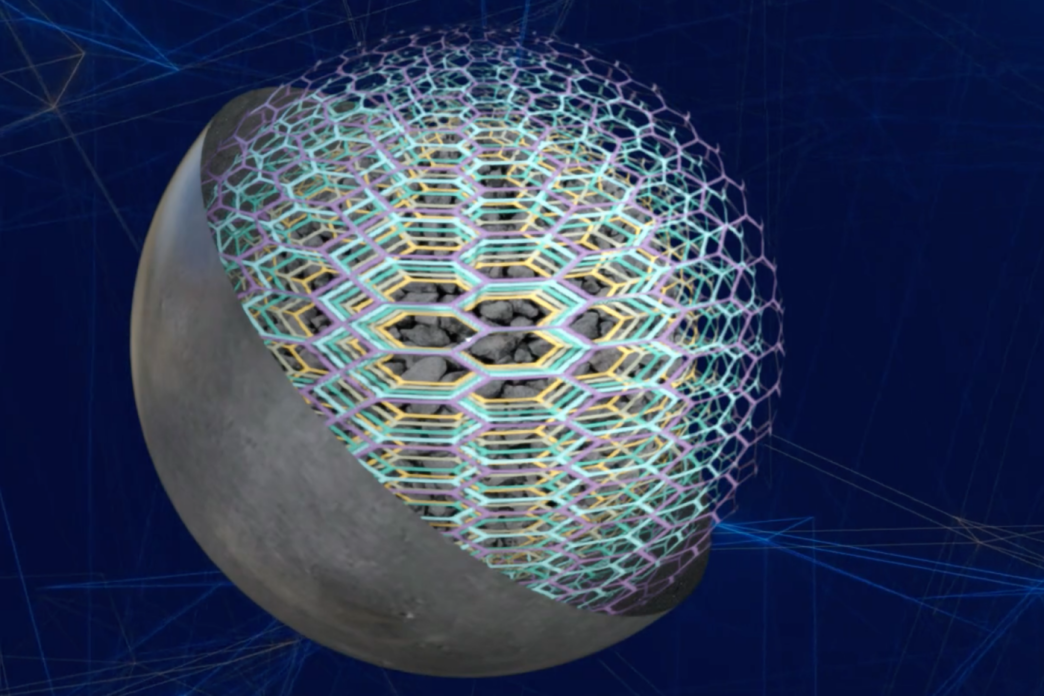
Paraclete Energy, a U.S.-based battery materials company, has presented a study on its silicon-based anode material, SILO Silicon, which it says could significantly reduce battery weight and improve electric vehicle (EV) range.
According to the company, SILO Silicon uses a polymer matrix design to offer advantages over traditional graphite anodes, including lower costs. Paraclete Energy estimates the cost of SILO Silicon at $35 per kilowatt-hour (kWh), compared to $53 per kWh for graphite. “Our data-driven approach demonstrates substantial reductions in battery weight and size alongside a notable increase in driving range,” said Jeff Norris, CEO of Paraclete Energy.
The study suggests that an 80 kWh battery pack could potentially decrease from 565 kg and 7,000 cells to 150 kg and fewer than 2,000 cells with SILO Silicon, a reduction in weight of 73%. The company also claims that a 300 kg battery configured with the material could deliver 160 kWh, increasing the range from 290 miles (466 km) to over 580 miles (932 km), while maintaining nearly 50% lower weight than conventional configurations.
The findings, which remain unverified by external sources, highlight potential advancements in battery technology. If proven, the material could address challenges in EV adoption by reducing costs and improving vehicle performance.
See Also
- U.S. Senators Urge Swift Action to Bridge 10 to 20-Year Gap in Battery Tech with China
- Paraclete Energy to Launch Advanced Silicon Anode Material for EV Batteries
- New Conductive Polymer Coating Could Revolutionize EV Batteries
- Forge Nano Begins Shipping High-Energy Prototype Battery Cells
- CATL Announces Massive Investment in Battery Recycling and Processing Park