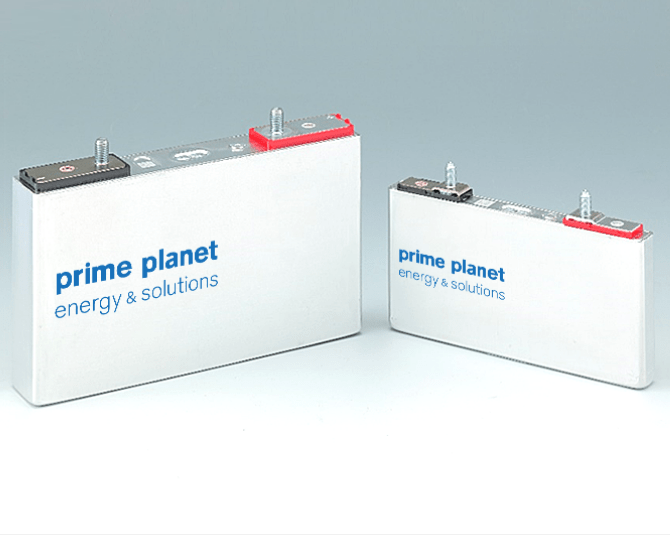
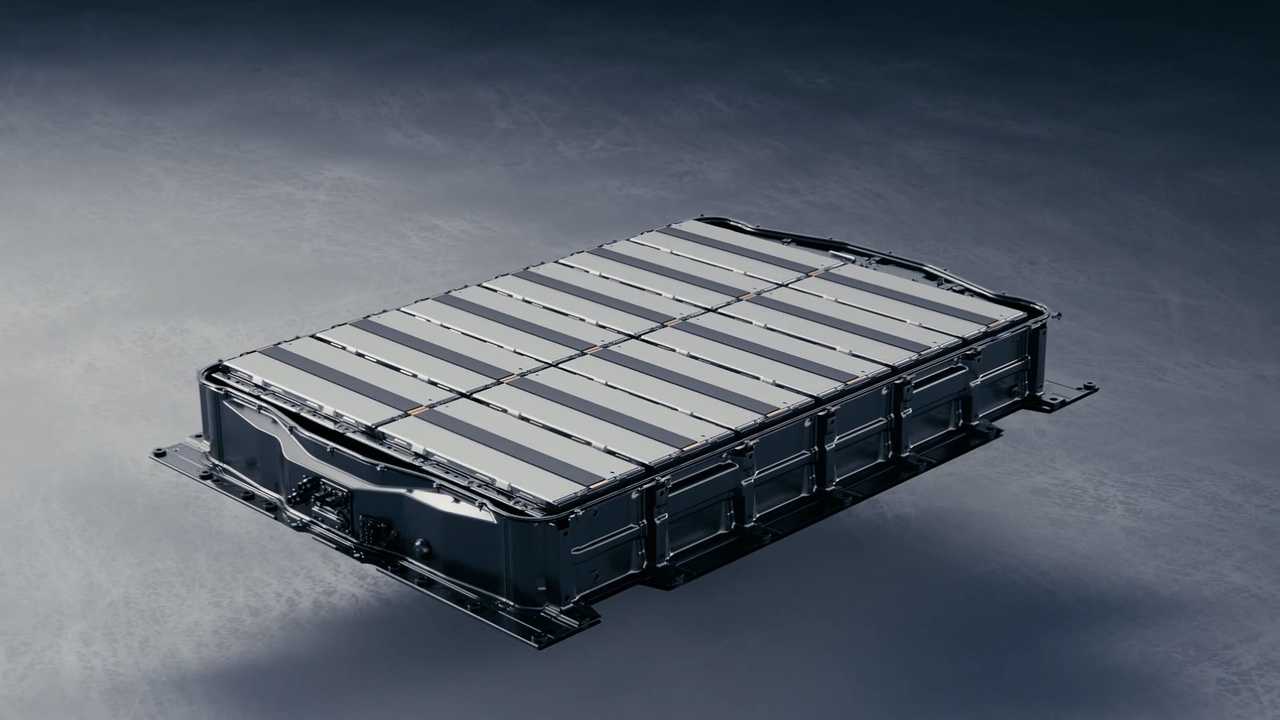
Prime Planet Energy & Solutions Inc, a joint venture of electric car (EV) battery manufacturers of Toyota Motor Corp and Panasonic Holdings Corp, is seeking new domestic manufacturing locations to offset soaring demand for EVs.
Prime Planet Energy & Solutions Inc President Hiroaki Koda said in an interview the company was looking for a new domestic manufacturing site that had an ocean port and access to clean energy.
Launching from Bloomberg, Prime Planet Energy & Solutions Inc., which officially starts operations in 2020, also plans to cut production costs by adopting Toyota’s Kaizen concept to increase productivity through small and continuous improvements, as it has to compete with larger battery manufacturers.
Lowering costs and making enough electric car batteries is key for Prime Planet amid rising raw material prices.
“The key is to what extent we can minimize costs and then how quickly we can roll out multiple production lines when the time comes,” said Koda.
Meanwhile Toyota, the world’s No. 1 automaker, has vowed to offer the “widest possible” range of powertrains to push cars in a more environmentally friendly way.
Toyota is still committed to spending around 4 trillion yen or 28.6 billion US dollars to switch its product line to electric power.
Prime Planet plans to cut costs by 60 percent by 2025, Koda added. Currently, the company makes EV batteries at its Himeji factory, a coastal city west of Tokyo.
Koda declined to elaborate on potential new manufacturing locations.
Toyota said in August it would invest $5.6 billion to increase production of EV batteries in Japan and the US.
Some of the money will flow to the Himeji factory while the other part will go to the factory in North Carolina, USA, United States.
There is also more room for cost-cutting and Prime Planet is working to “shorten lead times”, said Koda.
“We need to increase our competitiveness and offer lower prices because batteries are still a big part of electric vehicles,” he said.
Prime Planet’s share of the global EV battery market is minuscule compared to Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Ltd. and BYD Co. from China, and LG Energy Solution Ltd. from South Korea.
Panasonic takes 4th place with about 8.1 percent market share, according to Seoul-based SNE Research.
To catch up, the Japanese government is devising plans to expand global production capacity to 600 gigawatt-hours by 2030, of which 150 gigawatt-hours will be produced domestically.
Japan’s Organization Battery Association for Supply Chains has asked the state for about 2.3 trillion yen in aid, saying local companies need support to compete with foreign competitors.