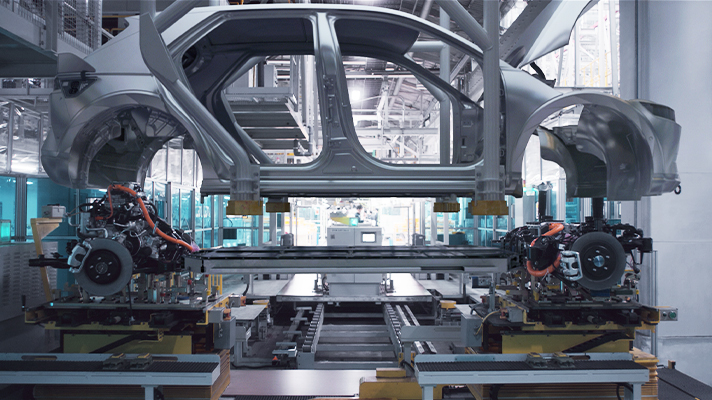
Hyundai Motor Company is reportedly exploring options to enhance its assembly line efficiency by taking cues from Tesla’s innovative gigacasting method. According to a recent report from Hankyung, Hyundai aims to integrate this groundbreaking approach into its production processes by the year 2026. Gigacasting, or hypercasting, has gained prominence in the automotive industry for its potential to reduce production costs, streamline manufacturing timelines, and even lighten vehicle weight, particularly advantageous for electric vehicles.
To accomplish this goal, Hyundai intends to increase its domestic investments in electrification and related components while transforming its existing manufacturing facilities into pivotal hubs for future vehicle production. A dedicated facility for casting, processing, and assembly is in the works, with construction set to commence next year, as per reports.
The gigacasting method, initially introduced with Tesla’s Model Y, employs a high-pressure die-casting machine to deliver molten aluminum into reusable casting molds. This innovative technique replaces the conventional practice of assembling chassis from numerous individual components, reducing it to only two or three larger parts. Notably, gigacasting eliminates the necessity for spot welding, as the final part emerges fully formed.
Estimates indicate potential cost savings of approximately 40%, a significant factor in Tesla’s ability to offer competitively priced vehicles. Hyundai is considering implementing this technique for the successor to its Ioniq 5 model, a move that could result in a lighter and more affordable electric vehicle.
Hyundai is not alone in its interest in Tesla’s pioneering production methods. German automaker Volkswagen has also expressed intentions to adopt gigacasting and plans to implement it across several of its factories. Furthermore, Toyota is actively exploring the possibility of incorporating hypercasting into its future electric vehicle lineup.
Both Volkswagen and Hyundai Motor Company are vying for leadership in the burgeoning electric vehicle sector, with a strategic focus on challenging Tesla’s dominance. Successful adoption of gigacasting could enable these manufacturers to offer more cost-effective electric vehicles, ultimately benefiting consumers.
In related developments, Hyundai is set to take control of the hydrogen fuel cell division initially established by its subsidiary, Hyundai Mobis. The automaker has expressed its commitment to expanding this division, potentially leading to a broader range of hydrogen-powered vehicles in the near future.
Lastly, Hyundai is contemplating the creation of a bespoke vehicle factory, highly adaptable and geared towards manufacturing unique cars that cannot be produced in existing facilities. This facility’s potential includes the production of limited edition models, convertibles, concept vehicles, and luxury cars, hinting at the possibility of high-end, one-of-a-kind offerings from the brand in the coming years. Only time will reveal the extent of Hyundai’s ambitions in this regard.