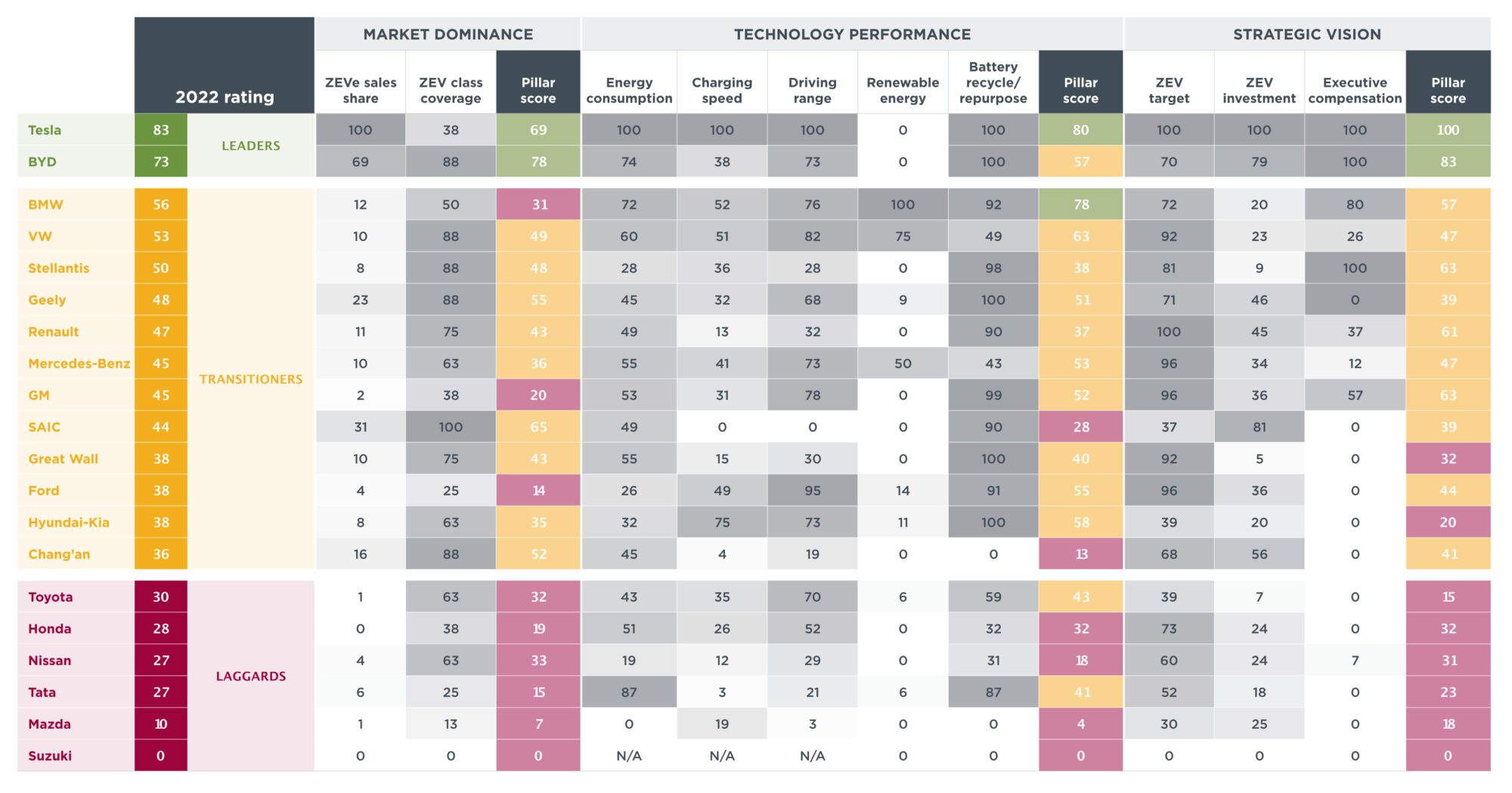
A groundbreaking report published by the International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT) evaluates the progress of the world’s top 20 automakers in embracing electric vehicles (EVs). Leading the pack is Tesla, the renowned electric vehicle pioneer, closely followed by the ambitious Chinese manufacturer, BYD.
This inaugural assessment of the electric drive system transition represents a significant milestone and will now be an annual release. The ICCT conducted an extensive analysis, gathering data from six key markets including China, the European Union, India, Japan, South Korea, and the United States. These six markets accounted for a substantial 89 percent of sales and 65 percent of global sales in 2022, from the 20 manufacturers under scrutiny.
The ICCT meticulously evaluated the performance, strategic vision, and current market position of these 20 automakers against a comprehensive set of criteria. Their analysis encompassed technical proficiency, existing market share, and the companies’ plans for future decarbonization. To facilitate this evaluation, the ICCT devised ten distinct metrics and relied on independent data gathered until the end of 2022.
Among the notable findings, Tesla emerged as the top-ranked manufacturer, earning the highest overall score from the ICCT. While Tesla exclusively produces zero-emission vehicles, it scored lower in certain criteria, such as the diversity of zero-emission models. Currently, Tesla offers only four model series. In second place is BYD, the ICCT’s description of the Chinese automaker as the “only long-established carmaker to focus on fully electric vehicles” highlights its rapid catch-up with Tesla. Both companies are acknowledged as leaders in the field.
BMW, Volkswagen, and Stellantis claim the midfield positions, with other prominent manufacturers like Geely, Renault, Mercedes, GM, Ford, and Hyundai-Kia also in this category. However, the ICCT’s rating reveals that six manufacturers among the top 20 globally, including Tata, Toyota, Honda, Nissan, Mazda, and Suzuki, trail behind their competitors. The ICCT remarks, “All five manufacturers headquartered in Japan and Tata, headquartered in India, are at the bottom of our rating. Nevertheless, most automakers excel in at least one metric, reflecting the intricate and diverse nature of the zero-emission vehicle transition and the various strategies adopted by manufacturers.”
Zifei Yang, the project manager and head of the ICCT Passenger Cars Programme, emphasizes the report’s objective of providing a data-driven and transparent analysis of automakers’ progress towards decarbonization. Yang asserts that the rating represents a forward-looking examination of manufacturers’ readiness for vehicle electrification, relying on independent data and analysis rather than company surveys or self-reporting. Furthermore, the ICCT has developed rating metrics aimed at tracking progress over time, with plans to update the rating annually.